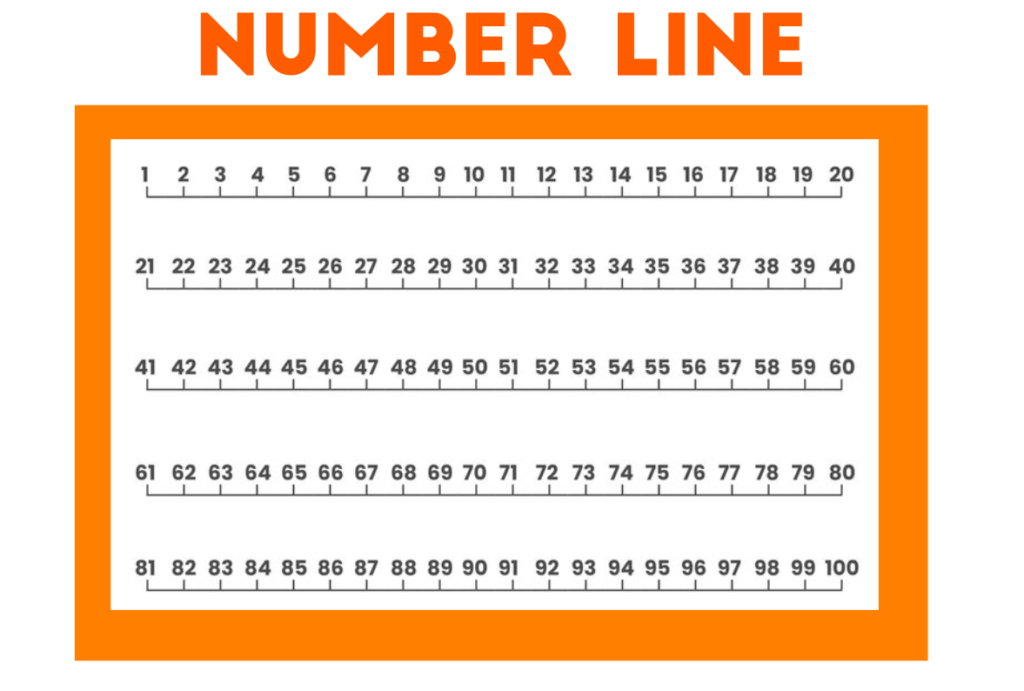
Ordering numbers is putting them into a sequence. This could be ‘ascending’, which means the numbers are getting larger. Ordering numbers is an important math skill for grade 1.
Contents
- 1 Top Methods Kids Number Ordering
- 2 But What Exactly Is Number Ordering?
- 3 Number Ordering in Ascending Order
- 4 Number Descending Order
- 5 Ordering Based On Size
- 6 Learning Number Ordering Through Rote
- 7 The Natural Order Of Numbers Is The Way They Are Written In Their Most Basic Form
- 8 When Comparing Two Numbers, The Larger One Comes First
- 9 When Counting, The Smallest Number Comes First
- 10 “One,” Mitsuru Whispered, Her Voice Trembling
- 11 When Listing Numbers In A Sequence, The Smallest Number Comes First
- 12 When Working With Fractions, The Smaller Number Comes First
- 13 Math Tricks For Ordering Numbers
- 14 Introducing The Basic Concept Of Number Ordering
- 15 Showing How To Use Math Tricks To Order Numbers Quickly And Easily
- 16 Final Thoughts
Top Methods Kids Number Ordering
There are many ways to order numbers for grade 1s, but the five most common ways are by magnitude, place value, Roman numerals, fractional values, and scientific notation.
But What Exactly Is Number Ordering?
Putting numbers into a series is called ordering. The numbers may be “ascending,” which indicates that they are increasing. The numbers could also be “descending,” which is when they go smaller. Numbers can be arranged in numerous ways.
There are many other ways to arrange numbers in a sequence, but the simplest method to do it is using the numbers 1, 2, 3, and 4. How do you start teaching kids this ability? What precedes it? How are the steps of the process taught? Continue reading to learn the answers to these and other questions.
Number Ordering in Ascending Order
Teaching students how to arrange the numbers in ascending order is the simplest technique to introduce sorting numbers.
This basically means arranging them in the proper sequence, such as 1, 2, 3, 4, etc.
The numbers are “ascending” because they are growing larger. It resembles moving “upward.”
But there are other ways to arrange integers in ascending order as well.
You can also choose from the following ascending number order types:
- The numbers rising and falling in units of 1, but not beginning with 1. Examples include 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9.
- A group of integers arranged in ascending order that are not all divisible by 1. For instance, the digits 3,6,14,17 and 14 could be ordered ascendingly as follows:
- A times table can have the numbers in an ascending order, such as 10, 20, 30, 40, or 50. Or perhaps 1, 2, 4, 6, or 8…
The aforementioned ascending order of numerals are the most typical sorts for young toddlers. Let’s continue to descend now.
Number Descending Order
This method of sorting integers is essentially the reverse of ascending. Going down is the same as descending. The most typical techniques for arranging integers in decreasing order are:
- Reversing direction after starting at a number. The most typical is 5,4,3,2,1,0, which is similar to a spaceship countdown.
- The same as the above, but not decreasing to 0 – for example, 8,7,6,5,4
- A series of decreasing random numbers, such as 9,6,5,2.
- A times table with the following numbers: 60, 50, 40, 30, 20, 10, 0.
Right, let’s move on to a really crucial part, which is how to educate children to order numbers.
Ordering Based On Size
This is unquestionably simpler than arranging numbers, and toddlers may experience it through play as early as age 3. They should try the following activities, for example:
- Putting clothing of various sizes up on a washing line. I enjoy wearing “giant’s clothes” (typical adult attire) and baby clothes.
- Weighing objects inside or outside. Examples include attempting to locate the stone or stick with the most weight.
- Sorting the playdough by length. Children construct and arrange models. Snakes, magic wands, worms, or broomsticks are a few suitable examples. One of the concepts in my article, “15 Playdough Math Games,” is this one.
- Playfully comparing which is longer/shorter, heavier/lighter
Learning Number Ordering Through Rote
This is quite significant. Children must be able to reliably recite the numbers in sequence before they can really begin to organize them.
The simplest approach to count by heart is to start at 1 and work your way up: 1, 2, 3, and so on. However, there are many different ways to rote count, so doing this first before ordering numbers that way is unquestionably the best course of action.
Among the best games for honing rote counting are:
- Dance while counting by playing music and chanting the numbers along with the beat.
- Marching while counting is encouraged!
- using a puppet, say the numerals
- Buddy Count: Face a partner, start with “one,” then “two,” and so on.
The Natural Order Of Numbers Is The Way They Are Written In Their Most Basic Form
The natural order of numbers is the way they are written in their most basic form. This is the order of operations that is used to solve mathematical problems.
The first step is to identify the operations that are being used in the problem. The order of these operations is Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication and Division (from left to right), Addition and Subtraction (from left to right).
When Comparing Two Numbers, The Larger One Comes First
When comparing two numbers, the larger one comes first. For example, if you are comparing the numbers 9 and 5, 9 is larger and comes first.
When Counting, The Smallest Number Comes First
Zen counted slowly to three in his head, then slowly raised his hand. Mitsuru watched the other boy, her heart beating in her chest. The two students stared at each other for a few moments before Zen finally spoke.
“One,” Mitsuru Whispered, Her Voice Trembling
Zen’s mouth quirked into a small smile. “Two,” he countered.
Mitsuru took a deep breath, trying to calm her racing heart. “Three,” she said.
Zen nodded and lowered his hand, signalling the end of the match. Mitsuru watched him for a few seconds before turning away and walking back to her seat.
When Listing Numbers In A Sequence, The Smallest Number Comes First
When listing numbers in a sequence for grade 1s, the smallest number comes first. This is called reverse order. For instance, when listing numbers from 1 to 10, the smallest number, 1, is listed first, and the largest number, 10, is listed last.
When Working With Fractions, The Smaller Number Comes First
When working with fractions, the smaller number always comes first. In the fraction 1/2, 1 is the smaller number and 2 is the larger number. In the fraction 2/3, 2 is the smaller number and 3 is the larger number.
When adding or subtracting fractions, the smaller number always comes first. In the fraction 4/5 + 3/5, 4 is the smaller number and 5 is the larger number. In the fraction 5/6 – 2/6, 5 is the smaller number and 6 is the larger number.
No matter which way you choose to order your numbers, make sure you are clear and consistent with your notation. This will make it easier for others to understand your work and calculations.
Math Tricks For Ordering Numbers
Math tricks can come in handy when you need to order numbers. Whether you are trying to order a list of items or just need to know which number is bigger or smaller, these tricks can help make the process a little simpler. Check out some of the tricks below to get started!
Introducing The Basic Concept Of Number Ordering
In mathematics, number ordering is the principle that some numbers are greater than others. This is often illustrated with the use of the number line, which goes from negative numbers to positive numbers. The greater the number on the number line, the greater that number is. This is also often represented with the use of the > symbol, which is read as “greater than.”
Showing How To Use Math Tricks To Order Numbers Quickly And Easily
There are a few math tricks that can be used to quickly and easily order numbers. For example, when dealing with larger numbers, it can be helpful to use the squares of the numbers to help line them up.
This can make it easier to see which number is bigger or smaller. Another trick that can be used is to group numbers together. This can make it easier to see which group of numbers is the biggest or smallest. By using these tricks, it can be much easier to quickly and easily order numbers.
Offering Some Tips And Tricks For Mastering Number Ordering
Number ordering can be tricky, but with a little practice, it can be easy to do. Here are a few tips to help you master number ordering:
1. Start with the smallest number and work your way up.
2. When you get to a number that is a multiple of 10, just add the number 10 to the end of the number.
3. If you get to a number that is a multiple of 100, just add the number 100 to the end of the number.
4. If you get to a number that is a multiple of 1000, just add the number 1000 to the end of the number.
These tips should help kids to master number ordering in no time!
Final Thoughts
Thanks for checking out this post on math tricks for grade 1 number ordering. I hope you found these tips helpful and that they make the process a little simpler. Have a great day!